public class Solution
extends Object
388 - Longest Absolute File Path\.
Medium
Suppose we have a file system that stores both files and directories. An example of one system is represented in the following picture:
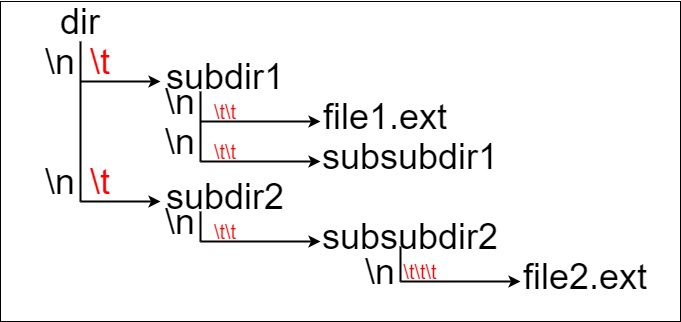
Here, we have `dir` as the only directory in the root. `dir` contains two subdirectories, `subdir1` and `subdir2`. `subdir1` contains a file `file1.ext` and subdirectory `subsubdir1`. `subdir2` contains a subdirectory `subsubdir2`, which contains a file `file2.ext`.
In text form, it looks like this (with ⟶ representing the tab character):
dir
⟶ subdir1
⟶ ⟶ file1.ext
⟶ ⟶ subsubdir1
⟶ subdir2
⟶ ⟶ subsubdir2
⟶ ⟶ ⟶ file2.ext
If we were to write this representation in code, it will look like this: `"dir
\tsubdir1
\t\tfile1.ext
\t\tsubsubdir1
\tsubdir2
\t\tsubsubdir2
\t\t\tfile2.ext"`. Note that the `'
'` and `'\t'` are the new-line and tab characters.
Every file and directory has a unique **absolute path** in the file system, which is the order of directories that must be opened to reach the file/directory itself, all concatenated by `'/'s`. Using the above example, the **absolute path** to `file2.ext` is `"dir/subdir2/subsubdir2/file2.ext"`. Each directory name consists of letters, digits, and/or spaces. Each file name is of the form `name.extension`, where `name` and `extension` consist of letters, digits, and/or spaces.
Given a string `input` representing the file system in the explained format, return _the length of the **longest absolute path** to a **file** in the abstracted file system_. If there is no file in the system, return `0`.
**Example 1:**
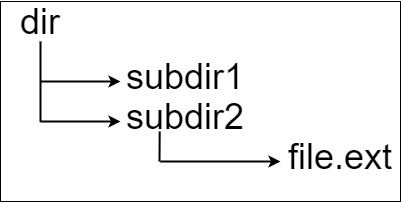
**Input:** input = "dir\n\tsubdir1\n\tsubdir2\n\t\tfile.ext"
**Output:** 20
**Explanation:** We have only one file, and the absolute path is "dir/subdir2/file.ext" of length 20.
**Example 2:**
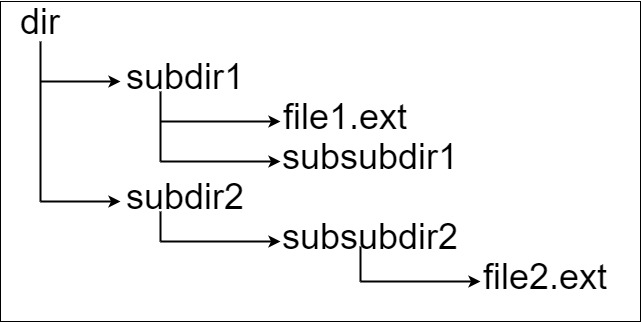
**Input:** input = input = "dir\n\tsubdir1\n\t\tfile1.ext\n\t\tsubsubdir1\n\tsubdir2\n\t\tsubsubdir2\n\t\t\tfile2.ext"
**Output:** 32
**Explanation:** We have two files: "dir/subdir1/file1.ext" of length 21 "dir/subdir2/subsubdir2/file2.ext" of length 32. We return 32 since it is the longest absolute path to a file.
**Example 3:**
**Input:** input = "a"
**Output:** 0
**Explanation:** We do not have any files, just a single directory named "a".
**Example 4:**
**Input:** input = "file1.txt
file2.txt
longfile.txt"
**Output:** 12
**Explanation:** There are 3 files at the root directory. Since the absolute path for anything at the root directory is just the name itself, the answer is "longfile.txt" with length 12.
**Constraints:**
* 1 <= input.length <= 104
* `input` may contain lowercase or uppercase English letters, a new line character `'
'`, a tab character `'\t'`, a dot `'.'`, a space `' '`, and digits.