public class Solution
extends Object
1632 - Rank Transform of a Matrix\.
Hard
Given an `m x n` `matrix`, return _a new matrix_ `answer` _where_ `answer[row][col]` _is the_ _**rank** of_ `matrix[row][col]`.
The **rank** is an **integer** that represents how large an element is compared to other elements. It is calculated using the following rules:
* The rank is an integer starting from `1`.
* If two elements `p` and `q` are in the **same row or column** , then:
* If `p < q` then `rank(p) < rank(q)`
* If `p == q` then `rank(p) == rank(q)`
* If `p > q` then `rank(p) > rank(q)`
* The **rank** should be as **small** as possible.
The test cases are generated so that `answer` is unique under the given rules.
**Example 1:**
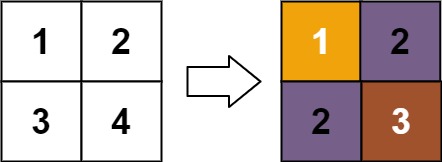
**Input:** matrix = \[\[1,2],[3,4]]
**Output:** [[1,2],[2,3]]
**Explanation:**
The rank of matrix[0][0] is 1 because it is the smallest integer in its row and column.
The rank of matrix[0][1] is 2 because matrix[0][1] > matrix[0][0] and matrix[0][0] is rank 1.
The rank of matrix[1][0] is 2 because matrix[1][0] > matrix[0][0] and matrix[0][0] is rank 1.
The rank of matrix[1][1] is 3 because matrix[1][1] > matrix[0][1], matrix[1][1] > matrix[1][0], and both matrix[0][1] and matrix[1][0] are rank 2.
**Example 2:**
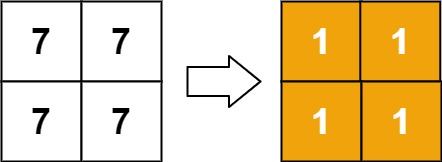
**Input:** matrix = \[\[7,7],[7,7]]
**Output:** [[1,1],[1,1]]
**Example 3:**
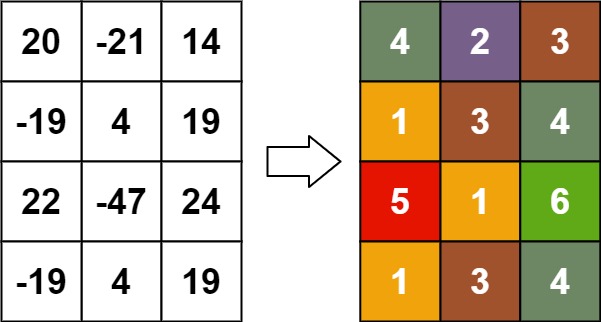
**Input:** matrix = \[\[20,-21,14],[-19,4,19],[22,-47,24],[-19,4,19]]
**Output:** [[4,2,3],[1,3,4],[5,1,6],[1,3,4]]
**Constraints:**
* `m == matrix.length`
* `n == matrix[i].length`
* `1 <= m, n <= 500`
* -109 <= matrix[row][col] <= 109