Class Solution
- java.lang.Object
-
- g1701_1800.s1766_tree_of_coprimes.Solution
-
public class Solution extends Object
1766 - Tree of Coprimes.Hard
There is a tree (i.e., a connected, undirected graph that has no cycles) consisting of
nnodes numbered from0ton - 1and exactlyn - 1edges. Each node has a value associated with it, and the root of the tree is node0.To represent this tree, you are given an integer array
numsand a 2D arrayedges. Eachnums[i]represents theithnode’s value, and eachedges[j] = [uj, vj]represents an edge between nodesujandvjin the tree.Two values
xandyare coprime ifgcd(x, y) == 1wheregcd(x, y)is the greatest common divisor ofxandy.An ancestor of a node
iis any other node on the shortest path from nodeito the root. A node is not considered an ancestor of itself.Return an array
ansof sizen, whereans[i]is the closest ancestor to nodeisuch thatnums[i]andnums[ans[i]]are coprime , or-1if there is no such ancestor.Example 1:
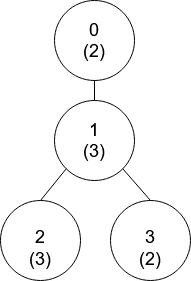
Input: nums = [2,3,3,2], edges = [[0,1],[1,2],[1,3]]
Output: [-1,0,0,1]
Explanation: In the above figure, each node’s value is in parentheses.
-
Node 0 has no coprime ancestors.
-
Node 1 has only one ancestor, node 0. Their values are coprime (gcd(2,3) == 1). - Node 2 has two ancestors, nodes 1 and 0. Node 1’s value is not coprime (gcd(3,3) == 3), but node 0’s value is (gcd(2,3) == 1), so node 0 is the closest valid ancestor.
-
Node 3 has two ancestors, nodes 1 and 0. It is coprime with node 1 (gcd(3,2) == 1), so node 1 is its closest valid ancestor.
Example 2:
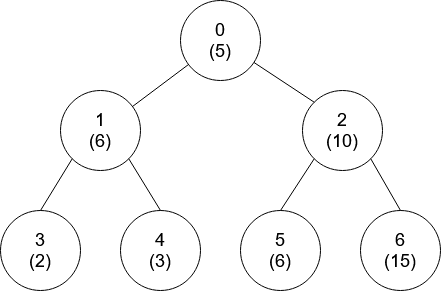
Input: nums = [5,6,10,2,3,6,15], edges = [[0,1],[0,2],[1,3],[1,4],[2,5],[2,6]]
Output: [-1,0,-1,0,0,0,-1]
Constraints:
nums.length == n1 <= nums[i] <= 501 <= n <= 105edges.length == n - 1edges[j].length == 20 <= uj, vj < nuj != vj
-
-
-
Constructor Summary
Constructors Constructor Description Solution()
-
Method Summary
All Methods Instance Methods Concrete Methods Modifier and Type Method Description int[]getCoprimes(int[] nums, int[][] edges)
-