Class Solution
java.lang.Object
g0601_0700.s0684_redundant_connection.Solution
684 - Redundant Connection\.
Medium
In this problem, a tree is an **undirected graph** that is connected and has no cycles.
You are given a graph that started as a tree with `n` nodes labeled from `1` to `n`, with one additional edge added. The added edge has two **different** vertices chosen from `1` to `n`, and was not an edge that already existed. The graph is represented as an array `edges` of length `n` where
edges[i] = [ai, bi] indicates that there is an edge between nodes ai and bi in the graph.
Return _an edge that can be removed so that the resulting graph is a tree of_ `n` _nodes_. If there are multiple answers, return the answer that occurs last in the input.
**Example 1:**
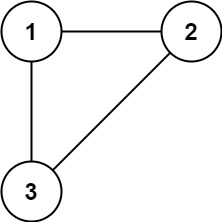
**Input:** edges = \[\[1,2],[1,3],[2,3]]
**Output:** [2,3]
**Example 2:**
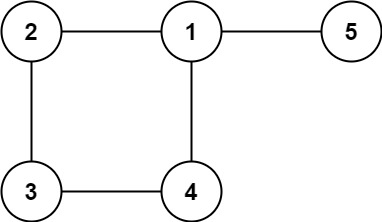
**Input:** edges = \[\[1,2],[2,3],[3,4],[1,4],[1,5]]
**Output:** [1,4]
**Constraints:**
* `n == edges.length`
* `3 <= n <= 1000`
* `edges[i].length == 2`
* 1 <= ai < bi <= edges.length
* ai != bi
* There are no repeated edges.
* The given graph is connected.-
Constructor Summary
Constructors -
Method Summary
-
Constructor Details
-
Solution
public Solution()
-
-
Method Details
-
findRedundantConnection
public int[] findRedundantConnection(int[][] edges)
-