Class Solution
java.lang.Object
g1501_1600.s1536_minimum_swaps_to_arrange_a_binary_grid.Solution
public class Solution
extends java.lang.Object
1536 - Minimum Swaps to Arrange a Binary Grid.
Medium
Given an n x n binary grid, in one step you can choose two adjacent rows of the grid and swap them.
A grid is said to be valid if all the cells above the main diagonal are zeros.
Return the minimum number of steps needed to make the grid valid, or -1 if the grid cannot be valid.
The main diagonal of a grid is the diagonal that starts at cell (1, 1) and ends at cell (n, n).
Example 1:
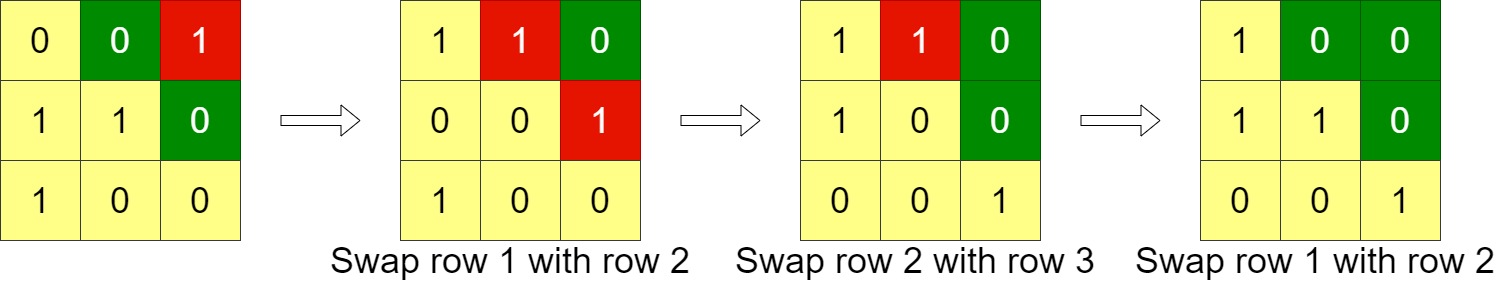
Input: grid = [[0,0,1],[1,1,0],[1,0,0]]
Output: 3
Example 2:
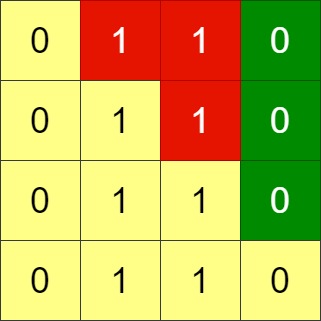
Input: grid = [[0,1,1,0],[0,1,1,0],[0,1,1,0],[0,1,1,0]]
Output: -1
Explanation: All rows are similar, swaps have no effect on the grid.
Example 3:
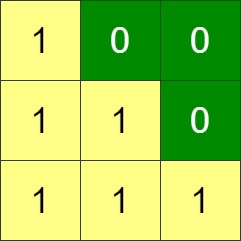
Input: grid = [[1,0,0],[1,1,0],[1,1,1]]
Output: 0
Constraints:
n == grid.length== grid[i].length1 <= n <= 200grid[i][j]is either0or1
-
Constructor Summary
Constructors -
Method Summary
Methods inherited from class java.lang.Object
clone, equals, finalize, getClass, hashCode, notify, notifyAll, toString, wait, wait, wait
-
Constructor Details
-
Solution
public Solution()
-
-
Method Details
-
minSwaps
public int minSwaps(int[][] grid)
-