Class Solution
Medium
A binary tree is named Even-Odd if it meets the following conditions:
- The root of the binary tree is at level index
0, its children are at level index1, their children are at level index2, etc. - For every even-indexed level, all nodes at the level have odd integer values in strictly increasing order (from left to right).
- For every odd-indexed level, all nodes at the level have even integer values in strictly decreasing order (from left to right).
Given the root of a binary tree, return true if the binary tree is Even-Odd , otherwise return false.
Example 1:
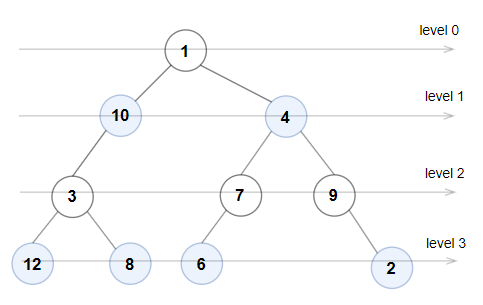
Input: root = [1,10,4,3,null,7,9,12,8,6,null,null,2]
Output: true
Explanation: The node values on each level are:
Level 0: [1]
Level 1: [10,4]
Level 2: [3,7,9]
Level 3: [12,8,6,2]
Since levels 0 and 2 are all odd and increasing and levels 1 and 3 are all even and decreasing, the tree is Even-Odd.
Example 2:
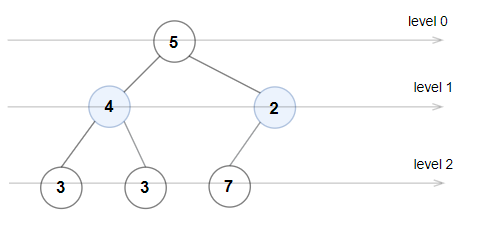
Input: root = [5,4,2,3,3,7]
Output: false
Explanation: The node values on each level are:
Level 0: [5]
Level 1: [4,2]
Level 2: [3,3,7]
Node values in level 2 must be in strictly increasing order, so the tree is not Even-Odd.
Example 3:
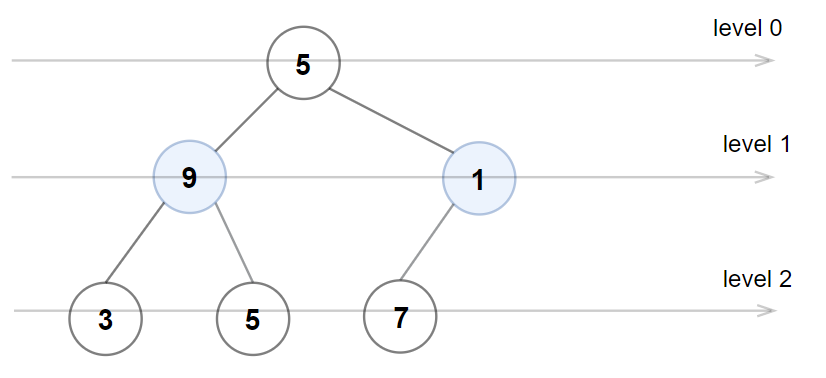
Input: root = [5,9,1,3,5,7]
Output: false
Explanation: Node values in the level 1 should be even integers.
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[1, 105]. 1 <= Node.val <= 106
-
Constructor Summary
Constructors -
Method Summary
Methods inherited from class java.lang.Object
clone, equals, finalize, getClass, hashCode, notify, notifyAll, toString, wait, wait, wait
-
Constructor Details
-
Solution
public Solution()
-
-
Method Details
-
isEvenOddTree
-