Class Solution
Hard
You are given an integer array nums of 2 * n integers. You need to partition nums into two arrays of length n to minimize the absolute difference of the sums of the arrays. To partition nums, put each element of nums into one of the two arrays.
Return the minimum possible absolute difference.
Example 1:
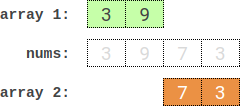
Input: nums = [3,9,7,3]
Output: 2
Explanation: One optimal partition is: [3,9] and [7,3]. The absolute difference between the sums of the arrays is abs((3 + 9) - (7 + 3)) = 2.
Example 2:
Input: nums = [-36,36]
Output: 72
Explanation: One optimal partition is: [-36] and [36]. The absolute difference between the sums of the arrays is abs((-36) - (36)) = 72.
Example 3:
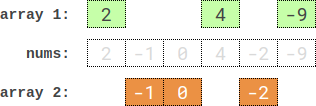
Input: nums = [2,-1,0,4,-2,-9]
Output: 0
Explanation: One optimal partition is: [2,4,-9] and [-1,0,-2]. The absolute difference between the sums of the arrays is abs((2 + 4 + -9) - (-1 + 0 + -2)) = 0.
Constraints:
1 <= n <= 15nums.length == 2 * n-107 <= nums[i] <= 107
-
Constructor Summary
Constructors -
Method Summary
Methods inherited from class java.lang.Object
clone, equals, finalize, getClass, hashCode, notify, notifyAll, toString, wait, wait, wait
-
Constructor Details
-
Solution
public Solution()
-
-
Method Details
-
minimumDifference
public int minimumDifference(int[] nums)
-