Class Solution
Medium
Given an m x n grid of characters board and a string word, return true if word exists in the grid.
The word can be constructed from letters of sequentially adjacent cells, where adjacent cells are horizontally or vertically neighboring. The same letter cell may not be used more than once.
Example 1:
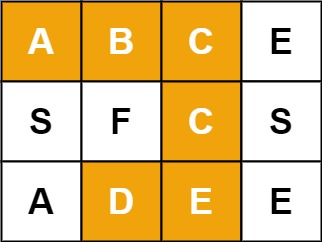
Input: board = [[“A”,“B”,“C”,“E”],[“S”,“F”,“C”,“S”],[“A”,“D”,“E”,“E”]], word = “ABCCED”
Output: true
Example 2:
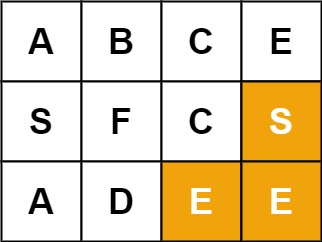
Input: board = [[“A”,“B”,“C”,“E”],[“S”,“F”,“C”,“S”],[“A”,“D”,“E”,“E”]], word = “SEE”
Output: true
Example 3:
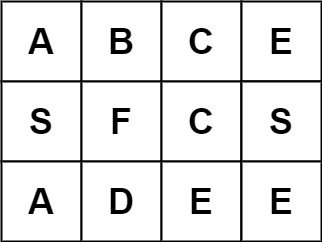
Input: board = [[“A”,“B”,“C”,“E”],[“S”,“F”,“C”,“S”],[“A”,“D”,“E”,“E”]], word = “ABCB”
Output: false
Constraints:
m == board.lengthn = board[i].length1 <= m, n <= 61 <= word.length <= 15boardandwordconsists of only lowercase and uppercase English letters.
Follow up: Could you use search pruning to make your solution faster with a larger board?
To solve the “Word Search” problem in Java with the Solution class, follow these steps:
- Define a method
existin theSolutionclass that takes a 2D character arrayboardand a stringwordas input and returnstrueif thewordexists in theboard. - Implement a backtracking algorithm to search for the
wordin theboard. - Iterate through each cell in the
board:- For each cell, call a recursive helper function
searchto check if thewordcan be found starting from that cell. - If
searchreturnstrue, returntrueimmediately.
- For each cell, call a recursive helper function
- Define the
searchmethod to perform the recursive backtracking:- Check if the current cell is out of bounds or if the current character in the
boarddoes not match the corresponding character in theword. - If any of the conditions are met, return
false. - Mark the current cell as visited by changing its value to a special character (e.g.,
#) to avoid revisiting it. - Recursively call
searchon neighboring cells (up, down, left, right) with the next character in theword. - After exploring all possible paths from the current cell, backtrack by restoring the original value of the current cell.
- Check if the current cell is out of bounds or if the current character in the
- If the
searchmethod reaches the end of theword, returntrue. - If no match is found after exploring all cells, return
false.
Here’s the implementation of the exist method in Java:
class Solution {
public boolean exist(char[][] board, String word) {
int m = board.length;
int n = board[0].length;
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
if (search(board, word, i, j, 0))
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
private boolean search(char[][] board, String word, int i, int j, int index) {
if (index == word.length())
return true;
if (i < 0 || i >= board.length || j < 0 || j >= board[0].length || board[i][j] != word.charAt(index))
return false;
char temp = board[i][j];
board[i][j] = '#'; // Mark as visited
boolean found = search(board, word, i + 1, j, index + 1) ||
search(board, word, i - 1, j, index + 1) ||
search(board, word, i, j + 1, index + 1) ||
search(board, word, i, j - 1, index + 1);
board[i][j] = temp; // Restore original value
return found;
}
}
This implementation uses backtracking to search for the word in the board, with a time complexity of O(M * N * 4^L), where M and N are the dimensions of the board and L is the length of the word.
-
Constructor Summary
Constructors -
Method Summary
-
Constructor Details
-
Solution
public Solution()
-
-
Method Details
-
exist
-